Interprocedural Analysis
Info
南京大学「软件分析」课程 Interprocedural Analysis 部分的学习笔记。
Motivation¶
为了处理 method calls,我们可以做最 conservative assumptions 来直接不管这个 method 的具体形态,但是这样会产生很大的 imprecision,于是,针对 method calls 这种特殊形态,我们需要一个 Interprocedural Analysis。
Call Graph Construction (CHA)¶
call graph: a representation of calling relationships in the program.
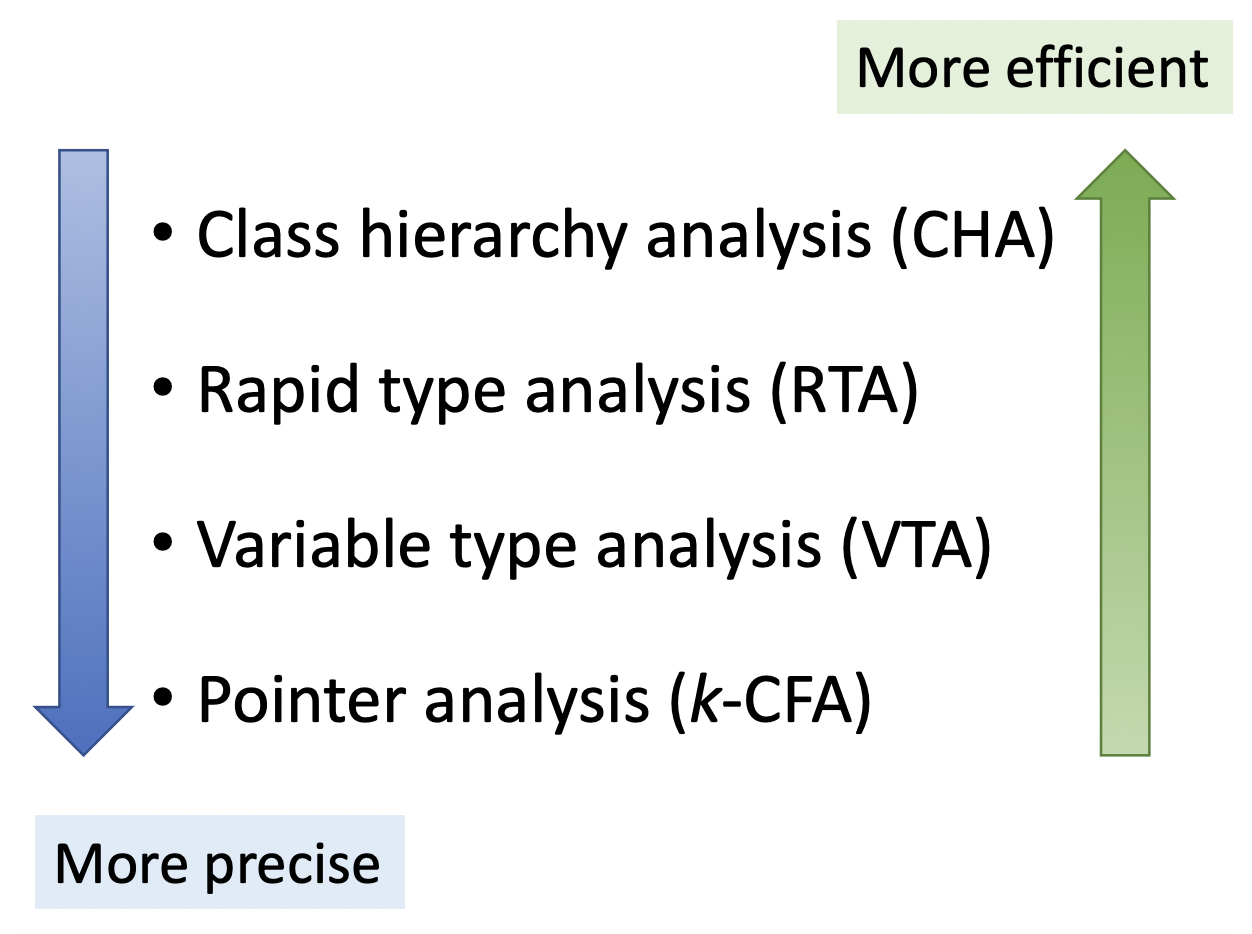
对于 OOPLs,call graph construction 主要有以下几种方法:
Method Call¶
在 Java 中,有 3 中 method calls,如下图所示
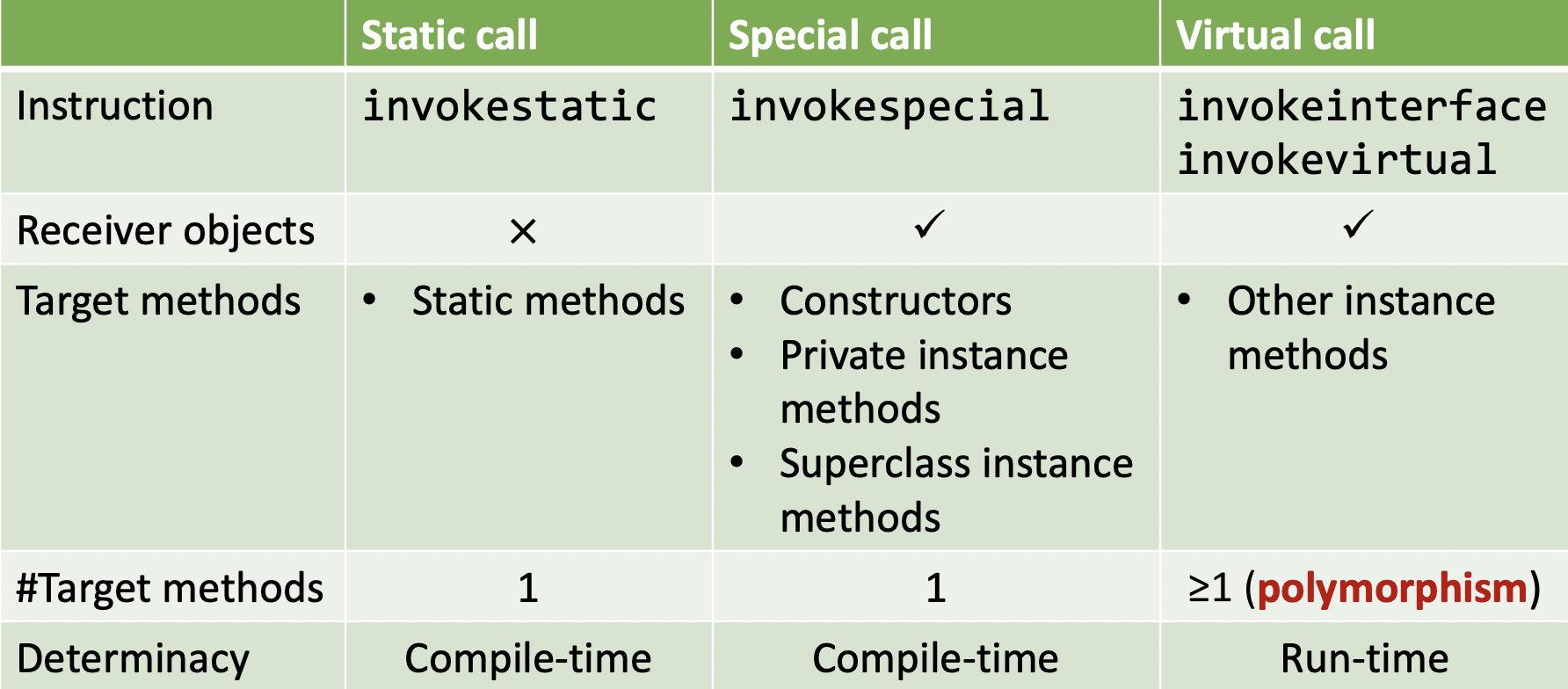
其中 virtual call 是最大的难点也是 call graph construction 的重点。
在 run-time,virtual call 基于以下两点决定调用哪个方法:
- type of the receiver object \(\to c\)
- method signature(identifier of a method) at the call site:
<C: T foo(P, Q, R)>\(\to m\) - signature = class type(C) + method name(foo) + descriptor(T, P, Q, R)
- descriptor: return type + parameter types
我们使用 \(Dispatch(c, m)\) 函数来描述 run-time 时 virtual call 的 dispatch 过程,实际就是递归向 parent 寻找对应的 method call 的过程。
Class Hierarchy Analysis¶
class hierarchy analysis (CHA) 是一种用来解决 method call 的方法,它需要整个程序的 class hierarchy information,并基于 declared type of receiver variable (\(a\)) of call site 和 \(a\) 可能指向任意子类或父类的假设来解决 virtual call。

CHA 只考虑 declared type of receiver variable
at the call-site 和它的 inheritance hierarchy,完全忽略 data- he control-flow 的信息,因此它具有 fast 的优势也有 imprecision 的劣势,它的一个运用场景就是 IDEA。
Call Graph Construction¶

Interprocedural Control-Flow Graph¶
CFG 展示的只是一个 individual method 的 structure,而 ICFG 则是在 CFG 的基础上加入了 call edges, return edges 来展示整个程序的 structure。
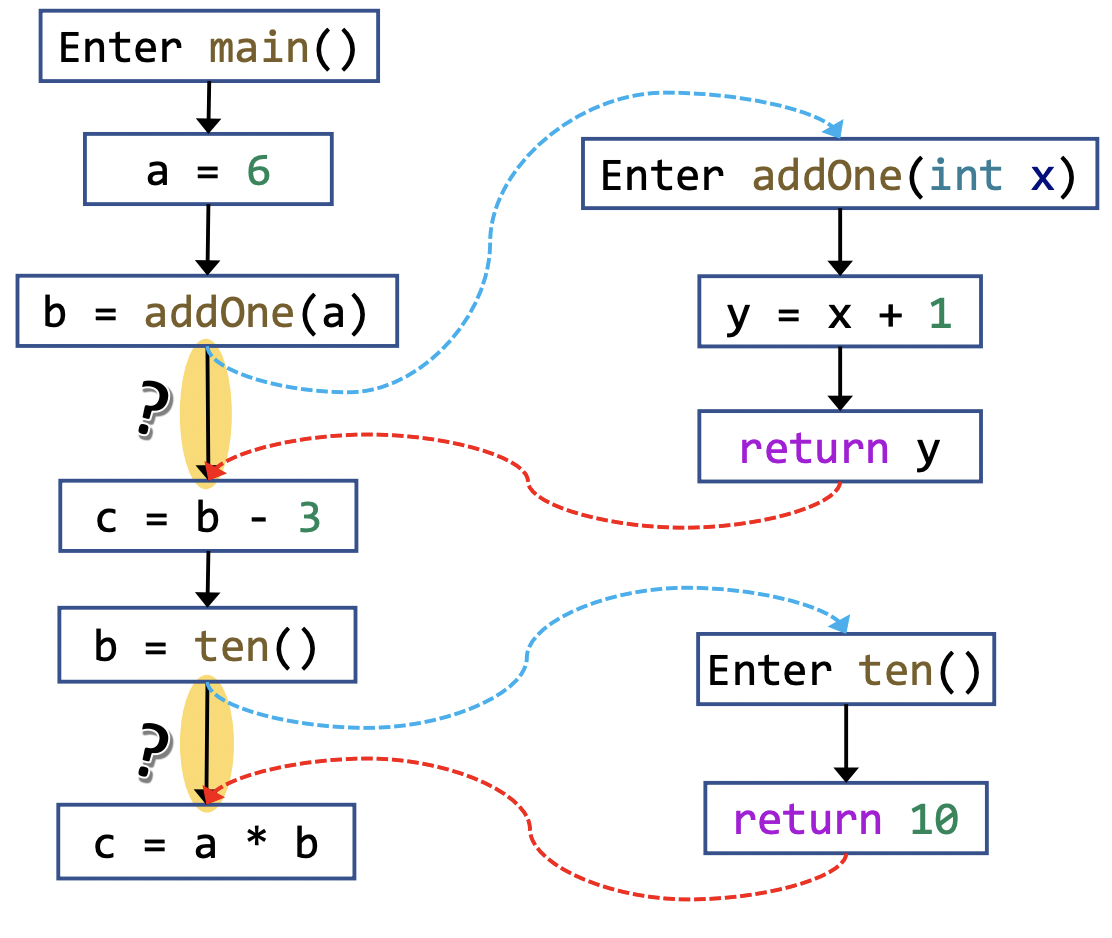
可以看到图中黄色部分的边连接了 call edge 和 return edge 的起点与终点,它的作用是让当前 CFG 中的 data-flow 信息可以直接流向下一个 BB 而不是从 call edge 然后经过一大段冗余的路径才到达下一个 BB。
Interprocedural Data-Flow Analysis¶
interprocedural data-flow analysis 就是基于 ICFG 对整个程序进行分析。相比于 intraprocedural 的 CFG,ICFG 加入了 call 和 return edges,相应的 transfer function 也要从 node transfer 加上 edge transfer。
- call edge transfer: transfer data flow from call site to the entry node of callee
- return edge: transfer: transfer data flow from the exit node of the callee to the return site
对于 intraprocedural 的 constant propagation,interprocedural 的 node transfer function 只在 call nodes 上有所不同:相比于直接将 LHS variable 设置为 NAC,我们先将这个 variable kill 掉,然后将其 flow 到 edge transfer,最后经由 return edge transfer 进行合并。
in summary:
- node transfer
- call nodes: identity
- other nodes: same as intraprocedural
- edge transfer
- normal edges: identity
- call-to-return edges: kill the LHS variable, then propagate others
- call edges: pass argument values
- return edges: pass return values
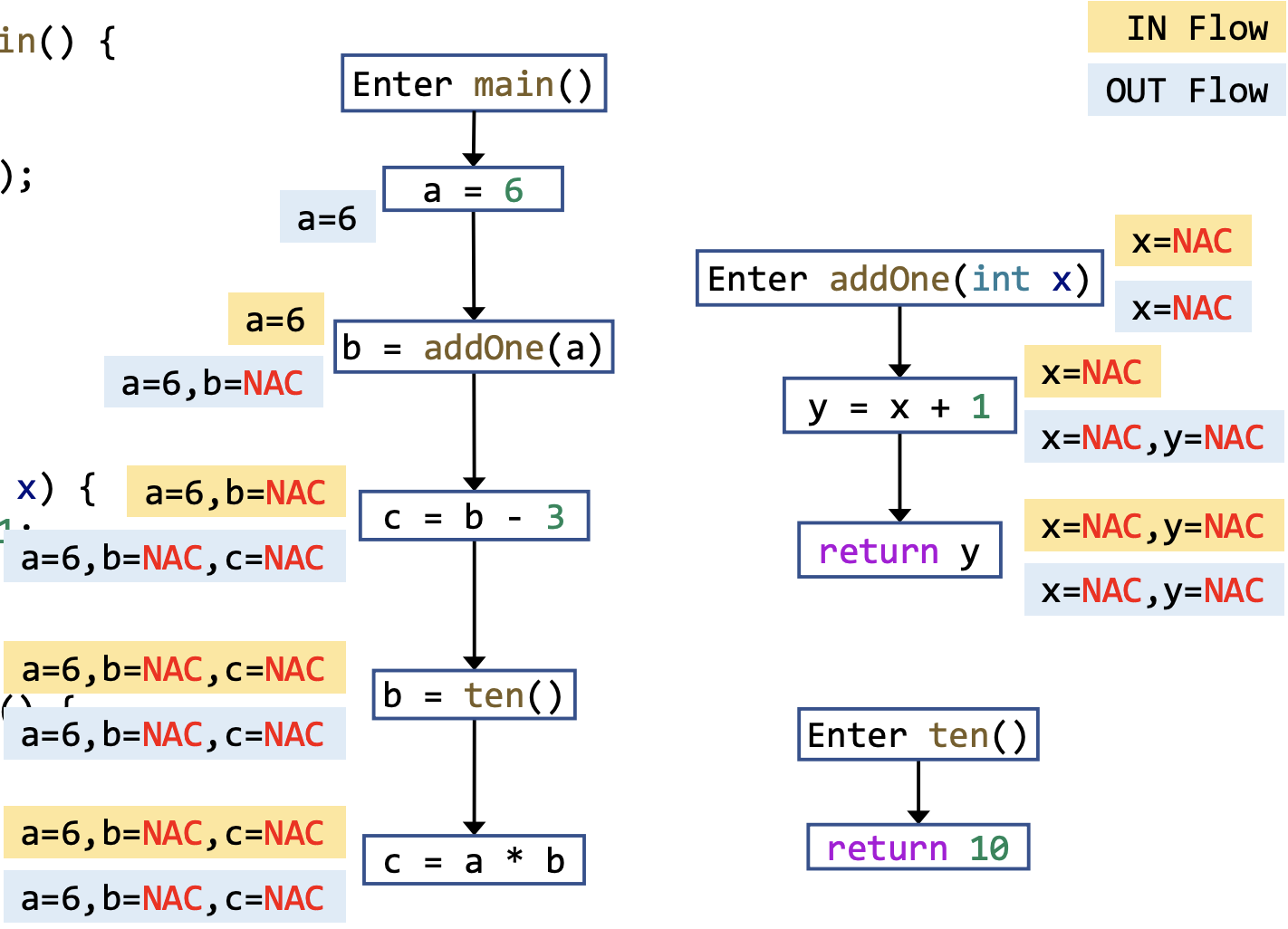
以下是一个 interprocedural data-flow analysis 的 example:
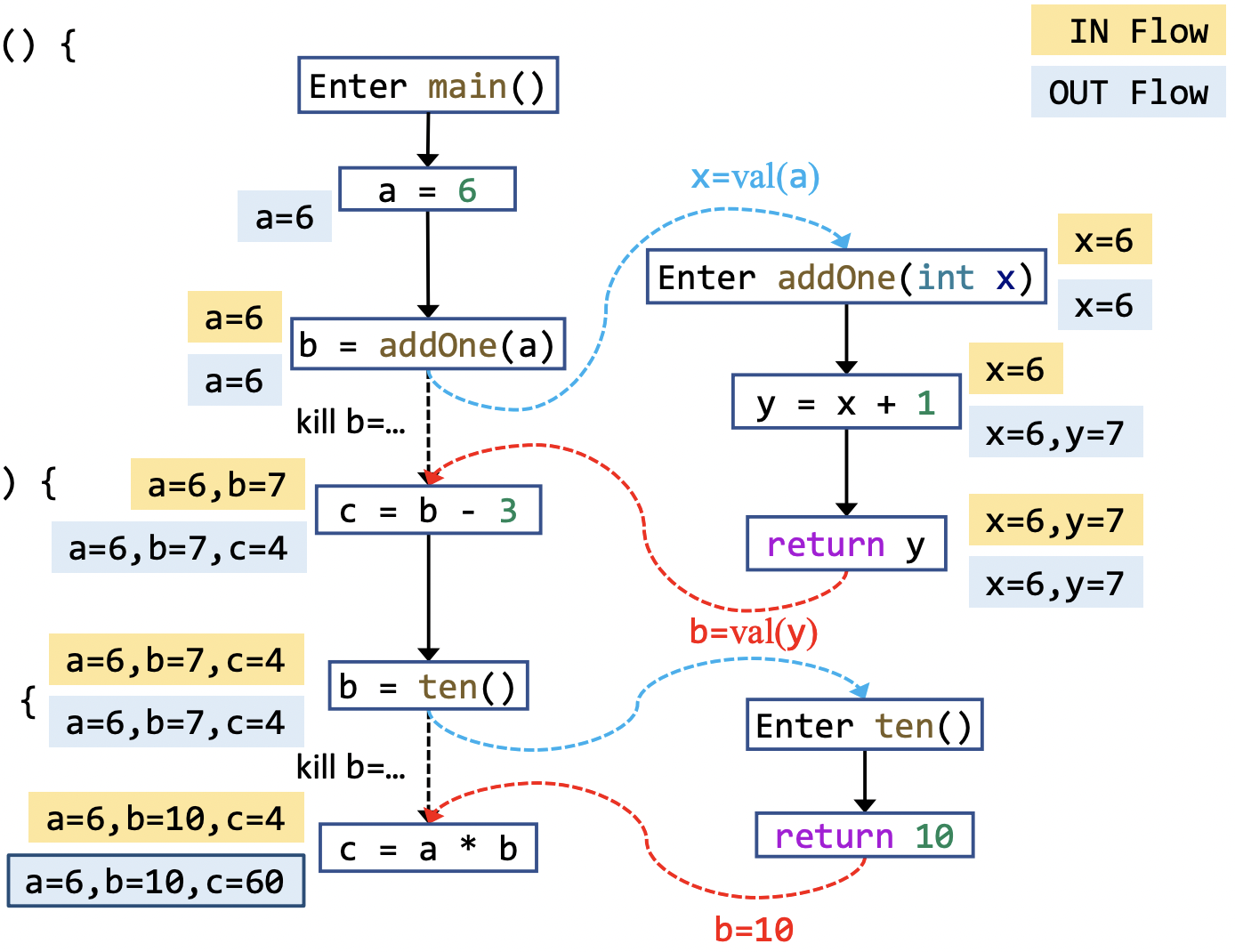
再与 intraprocedural data-flow analysis 进行,对比,很显然 interprocedural 的结果是更 precise 的。