Static Analysis for Security
Info
南京大学「软件分析」课程 Static Analysis for Security 部分的学习笔记。
security 指的是在存在 adversaries 的情况下能够成功达到一些 goals。
computer security 中非常重要的一个 topic 就是 information flow。
Information Flow Security¶
information flow security 的目的就是阻止通过阻止 unwanted information flow 来保护 information security。
保护 sensitive data 的方式主要有 access control 和 information flow security 两种。
- access control: a standard way
- 检查程序是否有权利 access 某些 information
- how information is accessed
- 不关心程序是如何使用这些 information 的
- information flow security: end-to-end
- 跟踪 information flow
- how information is propagated
"A practical system needs both access and flow control to satisfy all security requirements"
— D.Denning, 1976
information flow1 指的是如果有 information 从 variable \(x\) 流入 variable \(y\),就说存在信息流 \(x\to y\)。
而 information flow security 则通过将 variables 分为不同的 security levels、指定这些 levels 之间哪些 information flow 是允许的来达到 safe 的目的。
Security Levels (Classes)¶
不同 levels 的 classification 可以被划分成一个 topo 图的结构,更准确的说,可以被 modeled as lattice2.
Information Flow Policy¶
information flow security 用来限制在不同的 security levels 之间的 information flow。
一个经典的 policy 是 noninterference policy3,它要求通过 low variables 不能推断出任何 high information,具体来说就是禁止从 high variable 到 low variable 的 inforrmation flow,换句话说就是保证 information 只会在 lattice 上向上走。但是它允许了 low variable 到 high variable 的 information flow,这使得它仍然不能到达它的目的。
Confidentiality and Integrity¶
confidentiality 指的是阻止 secret information 泄漏,也就是上面的 noninterference policy 做到的。
而 integrity 指的是阻止 untrusted information 破坏 critical information4,有关的最广泛的 vulnerabilities 的造成原因就是 injection errors5 (SQL injection etc.)。
integrity 的广泛的定义是指以下三点:
- correctness: E.g. critical data 不应该被 untrusted data 破坏
- completeness (broader than consistency): E.g. 一个 DBS 应该完整保存整个 data
- consistency: E.g. 一个文件传输系统一个保证 sender 和 receiver 之间传输的文件内容是一致的
Explicit Flows and Covert Channels¶
通过直接 copy 进行的 information flow 称为 explicit flow。相应地,由 secret information 影响的 control flow 造成的 information flow 称为 implicit flow,implicit flow 同样可以产生 information leak。

上面这个程序存在一个从 secret 到 publik 的一个 implicit flow 并且会造成 leakage,但是并没有从 secret 到 publik 的 data flow,可以看出 information flow 和 data flow 的区别所在。
通过一个 computing system 来 signal information 的 mechanisms 被称为 channels。而目的不是 information transfer 的 channels 被称为 covert channels6。
常见的几种 covert channels 包括 implicit flows、termination channels、timing channels、exceptions。
由于 explicit flows 通常会比 covert channels 传递更多的 critical information,所以主要考虑 explicit flows。
Taint Analysis¶
taint analysis 是最常用的 information flow analysis。它将 data 分为两类:
- tainted data: 与 critical information 有关的 data,在 taint analysis 中将其打上一个 label
- untainted data
tainted data 的 sources 就被称为 sources,实践中它们往往是某些 methods (E.g. getPassword()) 的返回值。
taint analysis 的原理就是跟踪 tainted data,并观察它们是否有可能 flow 到某些 sensitive methods(可能造成 unsafe 的 methods,被称为 sinks)。
taint analysis 既能应用于 confidentiality 也能应用于 integrity 的检测:
- confidentiality
- source: source of secret data
- sink: leakage
- validation: information leaks
- integrity
- source: source of untrusted data
- sink: critical computation
- validation: injection errors
将 tainted data 看作 objects,sources 看作 allocation sites,可以看出来 taint analysis 要做的事就是 pointer analysis 的工作,因此我们可以沿用 pointer analysis 的方法来完成 taint analysis7。
在 domain and notations 中,我们只需额外增加一栏 tainted data,其余的保持不变:
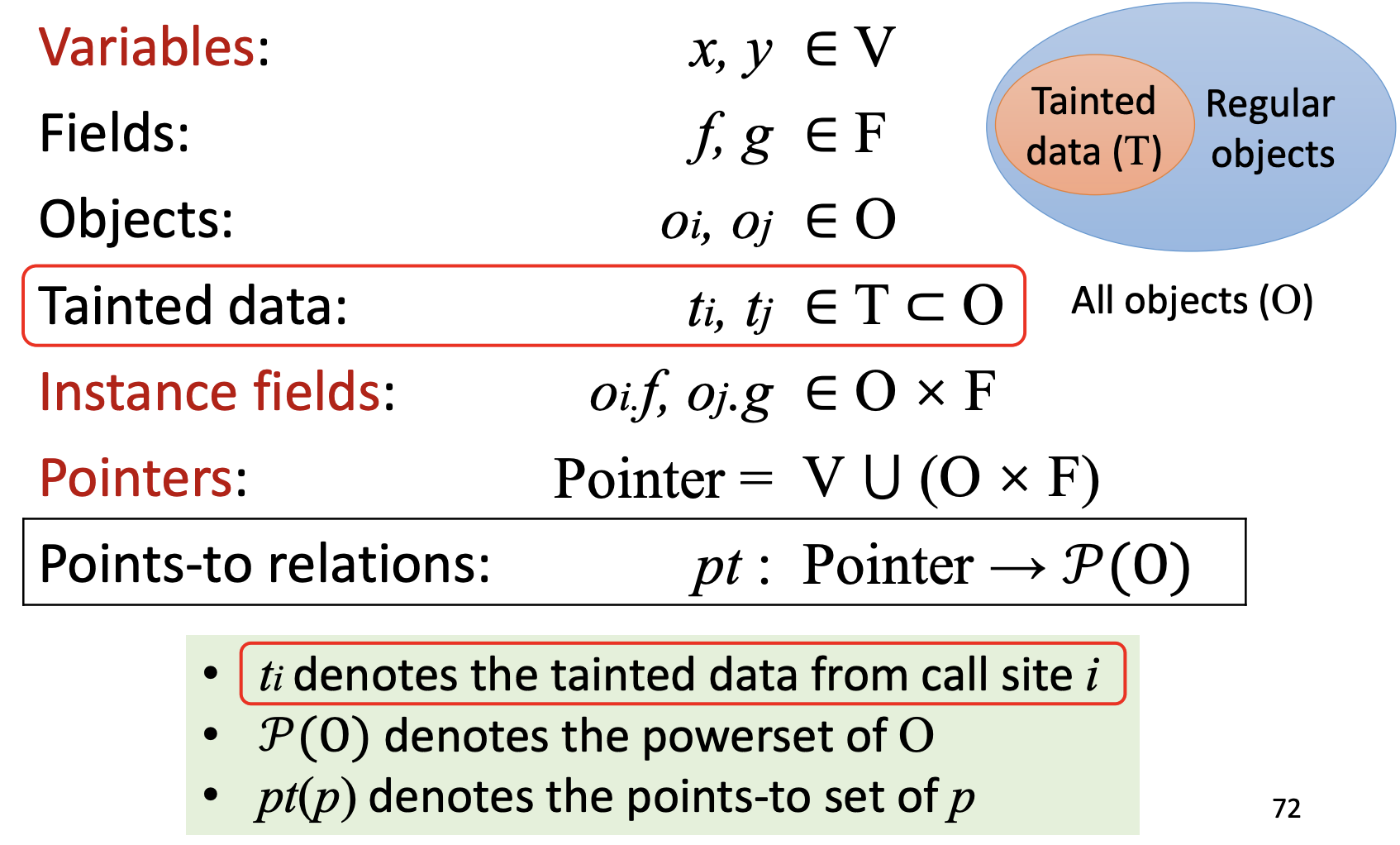
对于 inputs & outputs,taint analysis 需要我们输入 sources 和 sinks,然后会输出一系列由 source 和 sink calls 组成的 tuples 的 taintflows。
为了标记 tainted data 并输出 taintflows,taint analysis 对于 call 的 rules 也有所不同:
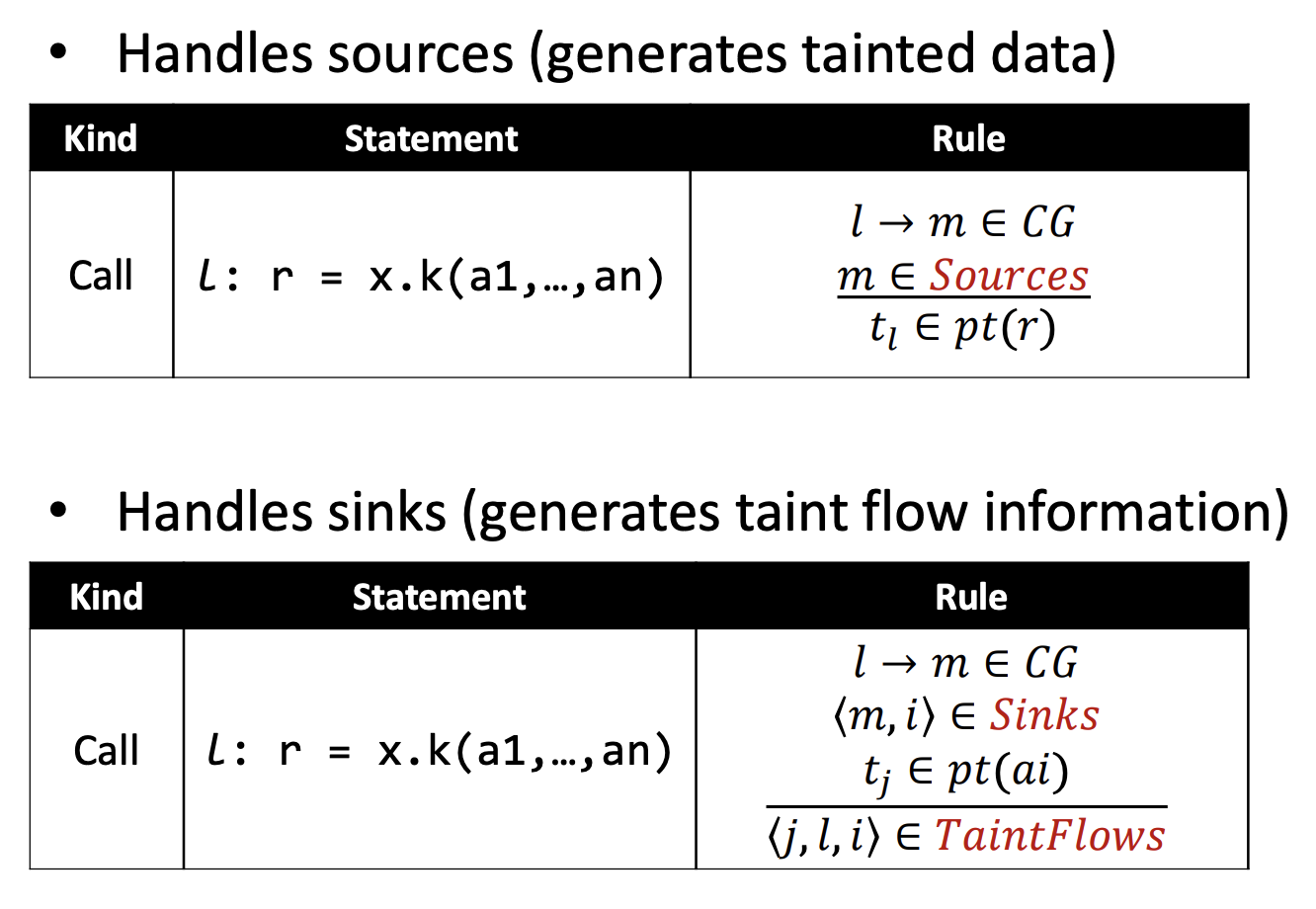
-
Dorothy E. Denning and Peter J. Denning, "Certification of Programs for Secure Information Flow". CACM 1977. ↩
-
Dorothy E. Denning, "A Lattice Model of Secure Information Flow". CACM 1976. ↩
-
J. A. Goguen and J. Meseguer, "Security policies and security models". S&P 1982. ↩
-
Ken Biba, "Integrity Considerations for Secure Computer Systems". Technical Report, ESD-TR-76-372, USAF Electronic Systems Division, Bed-ford, MA, 1977. ↩
-
National Vulnerability Database, https://nvd.nist.gov/ ↩
-
Butler W. Lampson, "A Note on the Confinement Problem". CACM 1973. ↩
-
Neville Grech and Yannis Smaragdakis, "P Taint: Unified Points-to and Taint Analysis". OOPSLA 2017. ↩